- Acadally
- 0 Comments
- 3172 Views
Gamification has revolutionised e-learning by injecting elements of gameplay into educational experiences, enhancing engagement and motivation. By leveraging game mechanics such as points, badges, and leaderboards, educators can transform passive learning into dynamic, interactive journeys. This approach not only captivates learners’ interest but also fosters collaboration, critical thinking, and skill development. Unlike traditional games, gamified learning apps retain the core educational content while integrating game elements to enhance user experience and learning outcomes. In this whitepaper, we explore the application of the Octalysis Framework, a comprehensive gamification model, to optimize learning outcomes in technology-based educational settings.
Gamification Designs
Gamification encompasses both human-focused and function-focused approaches. Human-focused gamification prioritises user experience, aiming to engage and motivate users by fulfilling their psychological needs and desires. On the other hand, function-focused gamification emphasises achieving specific objectives or outcomes, such as increasing productivity or driving user behaviour. Successful gamification strategies often strike a balance between these two perspectives, leveraging game-like elements to engage users while also achieving functional goals. Ultimately, the effectiveness of gamification depends on its ability to cater to both human desires and functional objectives, creating a compelling and impactful user experience.
Significance of Gamification in Learning
Traditional learning approaches can be passive and monotonous, leading to disengagement and hindered knowledge retention. Gamification injects elements of play and competition into the learning process, fostering a more active and intrinsically motivated learning experience. Research highlights the positive impact of gamification on various aspects of learning, including:
- Increased engagement and motivation
- Enhanced knowledge retention and recall
- Improved problem-solving skills
- Collaborative learning and teamwork
The Octalysis Framework: An Overview
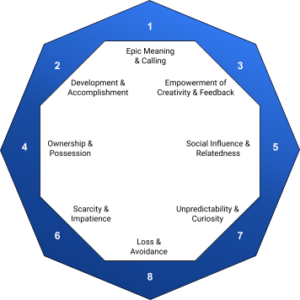
Developed by Yu-kai Chou, the Octalysis Framework offers a comprehensive eight-core drive model for understanding and implementing gamification strategies. These core drives encompass both intrinsic and extrinsic motivations, catering to a diverse range of learner preferences.
- Epic Meaning & Calling
- Development & Accomplishment
- Empowerment of Creativity & Feedback
- Ownership & Possession
- Social Influence & Relatedness
- Scarcity & Impatience
- Unpredictability & Curiosity
- Loss & Avoidance
Applying the Octalysis Framework to Learning
Applying the Octalysis Framework to learning involves leveraging its eight core drives to design engaging and effective educational experiences. It provides a versatile lens for educators and instructional designers to gamify learning experiences. Here’s how each core drive can be integrated:
Epic Meaning & Calling: This core drive involves instilling a sense of purpose and significance in learning activities. By framing educational goals within a broader narrative or mission, learners are motivated by a sense of meaning and impact.
Real-life situations often evoke Epic Meaning & Calling. For example, individuals may commit to environmental activism or advocate for social justice causes. Similarly, for a good cause, people contribute to ‘Wikipedia’ without monetary gain or stay loyal to Apple products.
Development & Accomplishment: Progression systems, achievements, and milestones appeal to the human desire for growth, mastery, and achievement. By providing clear goals and measurable progress indicators, educators can incentivize learners to actively engage with learning materials. For example, in role-playing games (RPGs), players immerse themselves in fictional worlds, building characters and navigating complex challenges using critical thinking. With the freedom to customise characters and explore intricate storylines, RPGs provide an immersive and expansive gaming experience that encourages players to actively engage with the game’s progression system.
Empowerment of Creativity & Feedback: Empowering creativity and providing feedback involves engaging users in a process where they can experiment and try out various combinations. It’s about giving them the freedom to explore their ideas and see how they unfold, while also receiving input on their creations. Engaging in activities such as playing with “Legos” (LEGO®) allows users to build, create, and experiment, observing the results of their efforts and adapting based on feedback. These experiences are enjoyable because they foster a continuous cycle of creativity and response, without constantly requiring new content to keep them interesting.
Ownership & Possession: Giving learners autonomy and control over their learning experience enhances their sense of ownership and investment in the process. Customization options, choice-based activities, and opportunities for self-directed learning empower learners to take responsibility for their educational journey. For example, games like “FarmVille™” create a sense of ownership by allowing players to own and manage their virtual farms, crops, and livestock. This ownership motivates players to protect and improve their farms, fostering a deeper level of engagement and commitment to the game.
Social Influence & Relatedness: Leveraging social dynamics, such as collaboration, competition, and community-building, taps into the human need for connection and belonging. Group activities, peer feedback, and multiplayer games create a supportive learning environment and foster social cohesion. For instance, in games like “PUBG™” (Player Unknown’s Battlegrounds), players collaborate with teammates, compete against opponents, and engage in community forums and events, fostering a sense of camaraderie and belonging within the gaming community.
Scarcity & Impatience: Introducing elements of scarcity, such as time constraints or limited resources, motivates learners to prioritise and focus their efforts. By creating a sense of urgency and anticipation, educators can drive engagement and prevent procrastination. For example, in the game “Candy Crush Saga,” players are given a limited number of lives or moves to complete each level. Once these resources are exhausted, players must wait for them to replenish over time or purchase additional lives using in-game currency. This scarcity of resources encourages players to strategize and carefully plan their moves to progress efficiently within the game. Additionally, limited-time events or special offers in “Candy Crush Saga” create a sense of urgency, enticing players to log in regularly to take advantage of exclusive rewards or bonuses before they expire.
Unpredictability & Curiosity: Surprising learners with unexpected challenges, rewards, or outcomes triggers curiosity and sustains engagement. Incorporating elements of mystery, exploration, and discovery cultivates a sense of wonder and encourages active participation. For example, in the game “Lords Mobile”, players encounter hidden treasures, secret locations, and unpredictable enemy attacks while exploring the vast open world. This unpredictability sparks curiosity and motivates players to continue exploring and discovering new experiences within the game. Similarly, gambling relies heavily on unpredictability, enticing players with the thrill of uncertain outcomes and contributing to addictive behaviour.
Loss & Avoidance: Fear of missing out, failure, or loss can be powerful motivators for action. By highlighting the consequences of inaction or suboptimal performance, educators can encourage learners to overcome obstacles and persist in their learning endeavours. For instance, in gaming, players often take actions to avoid loss, as failing to perform well can result in losing progress, points, or even facing “game over” scenarios. Additionally, the concept of Sunk Cost Tragedy/Fallacy is prevalent, where players feel compelled to continue playing despite diminishing returns or negative outcomes because they’ve invested significant time or resources into the game. This fear of “wasting” previous efforts can lead to prolonged engagement in an attempt to recoup perceived losses and validate past investments.

By strategically integrating these core drives into the design of learning experiences, educators can create gamified environments that captivate learners’ interest, foster intrinsic motivation, and optimize learning outcomes. Whether through gamified course modules, educational apps, or immersive simulations, the Octalysis Framework provides a versatile framework for designing engaging and effective learning experiences.
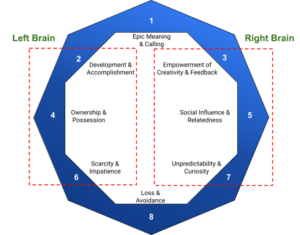
Based on the human motivation, these core drives are categorised as:
- Right Brain (Intrinsic Motivation): Focus on internal motivations like accomplishment, creativity, and social influence.
- Left Brain (Extrinsic motivation): Address external motivations such as rewards, recognition, and fear of missing out.
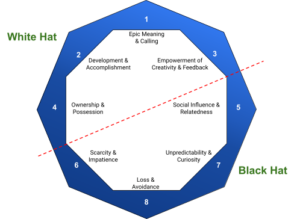
Similarly, based on the reinforcement, these core drives are categorised as:
- White Hat (Positive Reinforcement): Drives associated with feelings of gain, mastery, and progress.
- Black Hat (Negative Reinforcement): Drives fueled by avoiding loss, overcoming challenges, and defying expectations.
Case Study
An Octalysis analysis of “AcadAlly” reveals its strength across numerous of the 8 core drives.
Epic Meaning & Calling
Students discover and explore their strengths and growth (personal and academic) in a supportive non-judgmental space.
Development & Accomplishment
Students earn points and badges based on their engagement and performance in various activities on the “AcadAlly” application. They also gain targeted insights after quizzes and can visualise their academic journey through a virtual forest representing their progress. Students also receive personalized support to address identified learning gaps.
Empowerment of Creativity & Feedback
Students customise their avatars to reflect their style and preferences, as well as design a personalized space or dashboard that mirrors their individuality. They can upgrade or design their virtual forests.
Ownership & Possession
Students take ownership of their personalized learning journeys, actively engaging with quizzes and completing tasks within the application. This sense of responsibility drives them to advance their educational path, as they have control over various elements such as nurturing their virtual forest and managing their avatars.
Social Influence & Relatedness
Students engage with their classmates through features that facilitate community building and support.
Scarcity & Impatience
Students face limits on the number of activities they can attempt in a day, encouraging thoughtful and strategic engagement.
Unpredictability & Curiosity
“AcadAlly” is yet to work on this core.
Loss & Avoidance
Students maintain streaks by consistently engaging with the app and attempting activities daily.
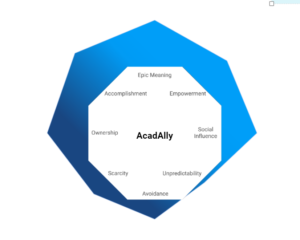
As we can see, “AcadAlly” incorporates all the white hat core drives for the positive reinforcement of the students while it also incorporates aspects of black hat core drives to some extent, to ensure sustained student engagement.
Limitation of Gamification for Learning Applications
The Octalysis framework’s utility diminishes when a learning application lacks a strong educational agenda. While it enhances engagement akin to gaming apps, learning objectives may be sidelined. The framework’s focus on gamification elements may overshadow pedagogical strategies crucial for effective learning experiences. Additionally, cultural variations in motivational drivers can limit its applicability. To ensure meaningful learning outcomes, a balanced approach, integrating Octalysis with instructional design principles, is essential for maximising educational impact while maintaining engagement.
For example, one prominent gaming company attempted to enter the educational gaming market but struggled to balance entertainment with educational substance. The resulting games lacked depth and failed to engage users effectively, underscoring the importance of meaningful learning experiences in gamified applications.
Summary
To summarize, gamification represents a transformative approach to learning, injecting elements of play and competition to enhance engagement and motivation. By leveraging strategies such as the Octalysis Framework, educators can design dynamic and effective learning experiences that cater to both intrinsic and extrinsic motivations. However, it’s important to recognize the limitations of gamification, particularly when gaming elements overshadow educational objectives. A balanced approach, integrating gamification with instructional design principles, is crucial for maximising educational impact while maintaining sustained engagement. Ultimately, gamification has the potential to revolutionise learning by fostering active participation, collaboration, and a lifelong passion for knowledge acquisition.
Author : Tarun Ahuja and Shilpi Singh